What is a wound?
The word ”wound” derived from the latin word ‘vulnus’ and describes the disturbance of normal continuity (for example skin) with or without tissue loss. It may accidentally happen due to an injury, a traumatic injury or an intentional surgical procedure.
The wounds can be classified according to their point of origin:
• Mechanical • Thermal • Chemical • Radiation • Skin Ulcer
Products used on wounds on skin and mucous membranes should not do the following:
• cause inflammation,
• work against human cells that help in wound healing process,
• be absorbed by the wound,
• cross the circulation system.
But what they should do, is to be effective against all resistant microorganisms.
What are the most important factors for wound healing?
• Improvement of the general condition of the patient
• Removal of pressure from wound surface
• Moisturizing the wound
• Removal of necrotic tissue with appropriate and sterile dressings, wiping with an antiseptic solution (working from wound center to the edges)
• Fighting infections
• If necessary, cover wounds with gauze or surgical biological bandages.
• Keep the wound temperature constant
• Follow-up blood values
• Assessment of the wound for infection, serosity and hematoma by daily opening
Wound Care Guide
Wounds can be classified by their appearance, source and state of contamination with pathogenic microorganisms. Wound classification facilitates assessment of the wound and enables early identification of potential risks.
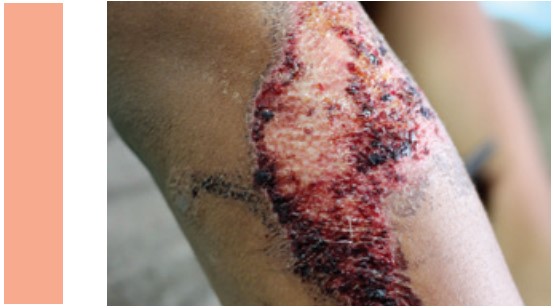
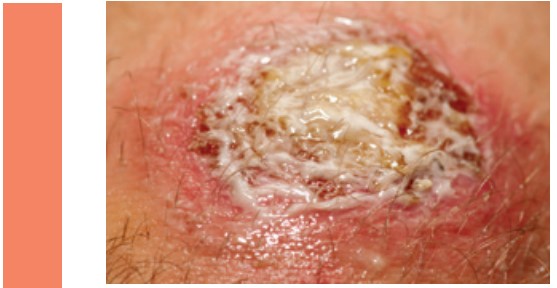
Wound Types: Contaminated wounds
Description: There are pathogenic microorganisms in the wound, but no indication of infection. Open wounds occurring immediately after traumata become contaminated wounds due to a major problem in the sterile technique which leads to excessive entry of bacteria into normally sterile body segments.
Product Suggestion: Actolind® Solüsyon + Actolind® w Jel
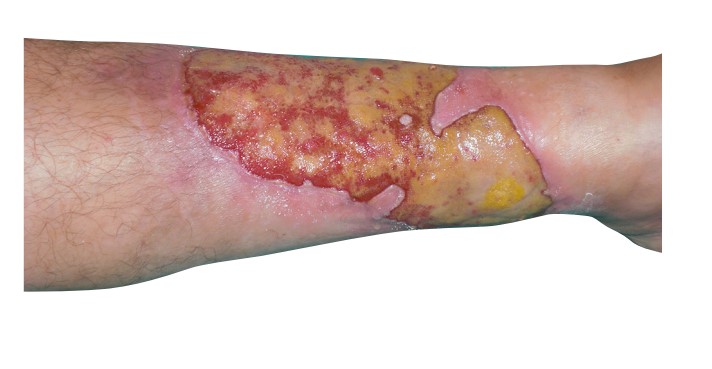
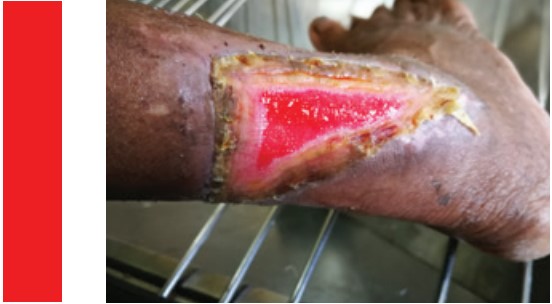
Wound Types: Burns
Description: “Burn” means the tissue damage caused by factors such as heat, electricity, chemicals, boiling water, flame, etc.
Extent of the tissue damage depends on the size of burnt area and the continuity of the causing factor.
Product Suggestion: Actolind® Solüsyon + Actolind® w Jel